VABYSMO met its primary endpoint of non-inferiority vs aflibercept 2 mg in the mean change from baseline in BCVA at year 1 (avg. of weeks 48, 52, and 56)1
Please see additional information on the Vision page
VABYSMO is the only treatment with flexible 1–4 month dosing1
VABYSMO can be administered via one of two regimens:1

*Although VABYSMO may need to be dosed as frequently as every 4 weeks after the first 4 doses, additional efficacy was not demonstrated in most patients compared to every 8 weeks.1
†If resolution of fluid based on CST is achieved, the interval may be modified based on CST and visual acuity in ≤4-week increment extensions, or ≤8-week increment reductions.1
After 4 loading doses, VABYSMO Q4W–Q16W patients received a median of 7 injections over 2 years (max of 21)1,2‡

Assessment and Limitations
The proportion of patients on each dosing interval was a prespecified secondary endpoint.2
- Not controlled for type 1 error, therefore, no formal conclusions can be drawn.
- Different inclusion/exclusion criteria and disease activity criteria may generate different results.
- The disease activity criteria utilized are not validated and the aflibercept arm was not dosed similarly.
‡This range excludes patients that did not complete the full 2-year protocol. The range for all enrolled patients was 1–21 total injections.1,2
§At week 56, 32% completed one full Q16W interval. 17% were treated on Q8W and/or Q4W (7% on Q4W only) through week 56.1
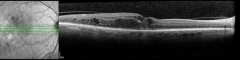
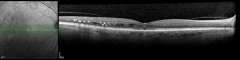
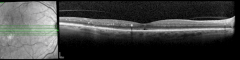
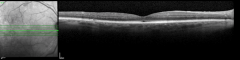
VABYSMO extended dosing intervals were achieved with control of CST and visual acuity1,2,18
Patient case: Extension to Q16W maintained through 2 years18
This patient was a participant with DME receiving VABYSMO in clinical trials. Individual results may vary.
No serious ocular adverse drug reactions were observed/reported in the treated eye.
BCVA=best corrected visual acuity; CST=central subfield thickness; DME=diabetic macular edema; Q4W=every 4 weeks; Q8W=every 8 weeks; Q12W=every 12 weeks; Q16W=every 16 weeks.
PEER PERSPECTIVES
What could flexible dosing mean for your patients and practice?
-
-
VABYSMO [package insert]. South San Francisco, CA: Genentech, Inc; 2024.
VABYSMO [package insert]. South San Francisco, CA: Genentech, Inc; 2024.
-
Data on file. South San Francisco, CA: Genentech, Inc.
Data on file. South San Francisco, CA: Genentech, Inc.
-
Baumal CR, et al. Presented at American Academy of Ophthalmology (AAO) 2022. Sep 30–Oct 03 2022.
Baumal CR, et al. Presented at American Academy of Ophthalmology (AAO) 2022. Sep 30–Oct 03 2022.
-
Tadayoni R, et al. Presented at Angiogenesis, Exudation, and Degeneration 2023. Feb 10–11 2023.
Tadayoni R, et al. Presented at Angiogenesis, Exudation, and Degeneration 2023. Feb 10–11 2023.
-
Regula JT, et al. EMBO Mol Med. 2016;8:1265–1288.
Regula JT, et al. EMBO Mol Med. 2016;8:1265–1288.
-
Saharinen P, et al. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017;16:635–661.
Saharinen P, et al. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017;16:635–661.
-
Warmke N, et al. J Diabetes Complications. 2016;30:1643-1650.
Warmke N, et al. J Diabetes Complications. 2016;30:1643-1650.
-
Fiedler U, et al. Trends Immunol. 2006;27(12):552–558.
Fiedler U, et al. Trends Immunol. 2006;27(12):552–558.
-
Avery RL, et al. Presented at American Association of Ophthalmology (AAO) 2022. Sept 30–Oct 03 2022.
Avery RL, et al. Presented at American Association of Ophthalmology (AAO) 2022. Sept 30–Oct 03 2022.
-
Heier J, et al. Lancet. 2022;399(10326):729–740.
Heier J, et al. Lancet. 2022;399(10326):729–740.
-
Guymer R, et al. Presented at Angiogenesis, Exudation, and Degeneration 2022. Feb 11–12 2022.
Guymer R, et al. Presented at Angiogenesis, Exudation, and Degeneration 2022. Feb 11–12 2022.
-
Tadayoni R, et al. Presented at Angiogenesis, Exudation, and Degeneration 2024. Feb 03 2024.
Tadayoni R, et al. Presented at Angiogenesis, Exudation, and Degeneration 2024. Feb 03 2024.
-
Khanani AM, et al. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2020;138(9):964–972.
Khanani AM, et al. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2020;138(9):964–972.
-
Sahni J, et al. Ophthalmology. 2019;126(8):1155–1170.
Sahni J, et al. Ophthalmology. 2019;126(8):1155–1170.
-
Wykoff C, et al. Lancet. 2022;399(10326):741–755.
Wykoff C, et al. Lancet. 2022;399(10326):741–755.
-
Heier JS, et al. Presented at American Academy of Ophthalmology Retina Subspecialty Day (AAO-SSD) 2021. Nov 12–13 2021.
Heier JS, et al. Presented at American Academy of Ophthalmology Retina Subspecialty Day (AAO-SSD) 2021. Nov 12–13 2021.
-
Goldberg R, et al. Presented at the Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology (ARVO) 2023. April 23–27 2023.
Goldberg R, et al. Presented at the Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology (ARVO) 2023. April 23–27 2023.
-
-
-
Baumal CR, et al. Presented at the Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology (ARVO) 2022. May 1–4 2022.
Baumal CR, et al. Presented at the Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology (ARVO) 2022. May 1–4 2022.
-